Understanding the Hair Color Wheel
The hair color wheel is a fundamental tool for both professional hairstylists and individuals seeking to enhance their hair color. It provides a systematic framework for understanding color relationships and predicting color outcomes in hair dyeing processes.

Primary Colors: The Foundation of Color
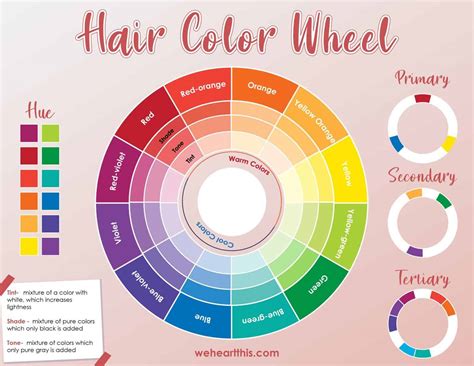
The primary colors of the hair color wheel are red, blue, and yellow. These colors cannot be created by mixing other colors and are considered the building blocks of all other hair colors.
Secondary Colors: Mixing Primaries
Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors. They include orange (red + yellow), violet (red + blue), and green (yellow + blue).
Tertiary Colors: Blending Secondaries
Tertiary colors are formed by mixing a primary color with a secondary color. They include red-orange, red-violet, blue-violet, blue-green, yellow-green, and yellow-orange.
Warm and Cool Colors
Colors can be classified as either warm or cool based on the sensations they evoke. Warm colors, such as red, orange, and yellow, create a feeling of warmth and energy. Cool colors, such as blue, violet, and green, give off a sense of coolness and relaxation.
Color Wheel Theory in Hair Dyeing
The hair color wheel serves as a guide for predicting the results of hair dyeing processes. By understanding the relationships between different colors, hairstylists can create desired hair colors while avoiding unexpected outcomes.
Color Matching and Correction
The hair color wheel is essential for matching hair colors to clients’ desired shades. Hairstylists use color theory to determine the target color and select the appropriate dyes to achieve it. In case of color corrections, the wheel helps identify the underlying color and determine the necessary corrective actions.
Color Placement and Blending
The hair color wheel guides hairstylists in strategically placing and blending colors to create depth, dimension, and highlights. They can combine warm and cool colors or use complementary colors to create unique and flattering effects.
Tips and Tricks
- Start with a small strand: Test the dye on a small section of hair first to ensure desired results before applying it to the entire head.
- Use a color chart: Consult a color chart to determine the best dye for your hair type and desired color.
- Consider your skin tone: Warm skin tones suit warm colors, while cool skin tones complement cool colors.
- Use multiple dyes: Combining different dyes can create a more natural and sophisticated look.
- Protect your hair: Use a hair mask before and after dyeing to minimize hair damage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overprocessing: Leaving the dye on for too long can lead to hair damage and unwanted color outcomes.
- Ignoring porosity: Hair porosity affects how well it absorbs dyes. Determine your hair’s porosity before dyeing.
- Using the wrong developer: The developer strength determines the lifting power of the dye. Choose the appropriate developer for your desired color level.
- Mixing incompatible dyes: Using dyes from different brands or chemical compositions can lead to unpredictable results.
- Not following instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing and applying hair dyes.
Applications Beyond Hair Dyeing
The hair color wheel has applications beyond traditional hair dyeing. It provides insights into color combinations and harmony that can be used in:
- Fashion: Clothing and accessory design by complementing or contrasting colors
- Interior Design: Creating balanced and aesthetically pleasing color schemes
- Makeup: Choosing flattering colors for makeup application
- Photography: Understanding color relationships for capturing the best shots
- Art and Design: Incorporating color theory into artistic creations
Conclusion
The hair color wheel is a valuable tool for understanding color relationships and applying color theory in hair dyeing processes. By mastering its concepts, hairstylists and individuals can achieve desired hair colors, correct color mishaps, and create unique and flattering hair color designs. Its principles can also be extended to various applications beyond hair dyeing, enriching our understanding of color and enhancing our ability to create harmonious and visually pleasing results in different fields.