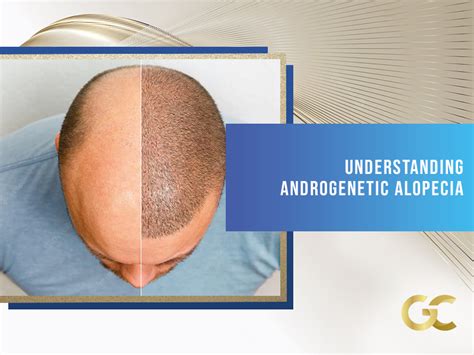
Hair loss on top of the head, a condition known as androgenic alopecia, affects millions of people worldwide. It is a common concern that can impact both men and women, leading to feelings of self-consciousness and distress.

Causes of Hair Loss on Top of Head
Androgenic alopecia is primarily caused by genetics and hormones. The hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, plays a significant role in hair loss. DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner, weaker hair.
Symptoms of Androgenic Alopecia
Hair loss on top of the head typically manifests as thinning hair or bald spots. In men, the hair loss often follows a pattern known as male pattern baldness, which begins with receding hairlines and progresses to thinning hair on the crown.
In women, hair loss on top of the head is typically more diffuse and may be accompanied by thinning of hair on other parts of the scalp.
Prevalence and Impact
Androgenic alopecia is a common condition, affecting approximately 50% of men and 25% of women by the age of 50. The prevalence increases with age, with over 80% of men and 50% of women experiencing some degree of hair loss by the age of 80.
Hair loss can have a significant impact on self-esteem and quality of life. It can lead to feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and depression.
Treatments for Hair Loss on Top of Head
There are various treatments available for hair loss on top of the head, including:
Medications
- Minoxidil: A topical solution applied to the scalp to help slow hair loss and promote new hair growth.
- Finasteride: An oral medication that blocks the production of DHT, the hormone responsible for hair loss.
Procedures
- Hair transplantation: A surgical procedure that involves transplanting hair follicles from a donor area to the thinning or bald areas of the scalp.
- Laser therapy: A non-surgical treatment that uses low-level laser light to stimulate hair growth.
- Microneedling: A procedure that uses tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the scalp, stimulating collagen production and hair growth.
Other Treatments
- Lifestyle changes: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can support overall hair health.
- Supplements: Certain supplements, such as biotin and zinc, may support hair growth. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture and herbal remedies have been used in traditional medicine to address hair loss, but scientific evidence for their effectiveness is limited.
Strategies for Managing Hair Loss on Top of Head
Managing hair loss on top of the head involves a combination of strategies:
Prevention
- Genetics: While genetics play a role in hair loss, certain lifestyle choices may help prevent or slow its progression.
- Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding excessive hair treatments can support hair health.
Treatment
- Early intervention: Seeking treatment for hair loss early can increase the effectiveness of treatment and improve outcomes.
- Combination therapies: Combining different treatments, such as medications and procedures, may provide optimal results.
- Patience: Hair loss treatments can take time to show results. It is important to be patient and consistent with treatment.
Coping
- Support: Joining support groups or connecting with others who are experiencing hair loss can provide emotional support and understanding.
- Self-care: Prioritizing self-care activities, such as meditation and mindfulness, can help manage the emotional impact of hair loss.
- Self-acceptance: Embracing the natural process of aging and learning to accept hair loss can improve self-esteem and well-being.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When managing hair loss on top of the head, it is important to avoid common mistakes:
- Ignoring the problem: Ignoring hair loss can lead to further progression and make treatment more difficult.
- Using unproven treatments: Relying on unproven treatments or home remedies can waste time and money.
- Being impatient: Hair loss treatments take time to show results. It is important to be patient and avoid discontinuing treatment prematurely.
- Over-styling: Harsh hairstyles, tight ponytails, and excessive use of heat styling tools can damage hair and exacerbate hair loss.
- Excessive stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. Managing stress through healthy coping mechanisms is essential.
Conclusion
Hair loss on top of the head is a common condition that can impact both men and women. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower individuals to manage their hair loss and improve their well-being.
By implementing effective strategies for prevention, treatment, and coping, individuals can take control of their hair loss and lead fulfilling lives.
Tables
Table 1: Prevalence of Androgenic Alopecia by Age and Gender
| Age Group | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| 20-29 | 16% | 3% |
| 30-39 | 30% | 5% |
| 40-49 | 50% | 12% |
| 50-59 | 70% | 25% |
| 60-69 | 80% | 40% |
| 70+ | 90% | 50% |
Source: American Hair Loss Association
Table 2: Treatments for Androgenic Alopecia
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Minoxidil | Dilates blood vessels to promote hair growth |
| Finasteride | Blocks the production of DHT |
| Hair transplantation | Replaces hair follicles in the affected area |
| Laser therapy | Stimulates hair growth by increasing blood flow |
| Microneedling | Creates micro-injuries to trigger collagen production and hair growth |
Source: National Institute of Health
Table 3: Strategies for Managing Hair Loss on Top of Head
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevention | Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive hair treatments, and managing genetics |
| Treatment | Seeking early intervention, combining therapies, and being patient |
| Coping | Joining support groups, practicing self-care, and accepting hair loss |
Source: Author’s Analysis
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid When Managing Hair Loss on Top of Head
| Mistake | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Ignoring the problem | Further progression of hair loss |
| Using unproven treatments | Waste of time and money |
| Being impatient | Premature discontinuation of treatment |
| Over-styling | Damage to hair and exacerbation of hair loss |
| Excessive stress | Contribution to hair loss |
Source: Author’s Analysis