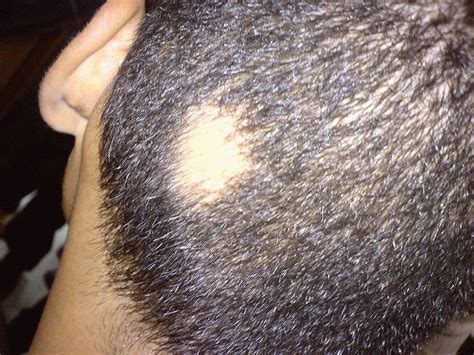
Alopecia Areata is one of the most difficult conditions to treat
Have you ever noticed round or oval patches of hair loss on your scalp? If so, you may have alopecia areata (AA), an autoimmune disease which causes hair to fall out in patches. AA can affect people of all ages, races, and sexes, but it is most common in women between the ages of 20 and 40. According to the National Alopecia Areata Foundation, approximately 6.6 million people in the United States have AA. That means that about 1 in 500 people will develop AA at some point in their lives. It can be a very isolating and embarrassing condition, as people with AA often feel self-conscious about their appearance.

What causes alopecia areata?
The exact cause of AA is not known, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disease. This means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, causing them to stop producing hair. Research is revealing that AA may be linked to many other autoimmune and genetic conditions.AA can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Stress
- Illness
- Certain medications
- Trauma
There is no cure for AA, but there are a number of treatments that can help to slow down or stop hair loss. These treatments include:
- Topical medications
- Oral medications
- Light therapy
- Surgery
How to cope with alopecia areata
If you have AA, there are a number of things you can do to cope with the condition. These include:
- Joining a support group
- Talking to a therapist
- Wearing a wig or hairpiece
- Shaving your head
It is important to remember that you are not alone. There are many people who have AA, and there are a number of resources available to help you cope with the condition.
Alopecia Areata: Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about alopecia areata:
- What is the prognosis for alopecia areata?
- Can alopecia areata be prevented?
- What are the treatments for alopecia areata?
- How can I cope with alopecia areata?
For more information on alopecia areata, please visit the website of the National Alopecia Areata Foundation.
10 Things You Didn’t Know About Alopecia Areata
Here are 10 things you didn’t know about alopecia areata:
- AA is the most common autoimmune disease affecting the hair.
- AA can affect people of all ages, races, and sexes.
- AA is not contagious.
- There is no cure for AA, but there are a number of treatments that can help to slow down or stop hair loss.
- AA can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, illness, certain medications, and trauma.
- There are a number of ways to cope with AA, including joining a support group, talking to a therapist, wearing a wig or hairpiece, and shaving your head.
- AA is not a sign of weakness or illness.
- People with AA can live full and happy lives.
- There is hope for a cure for AA.
- You are not alone.
20 Tips for Living with Alopecia Areata
Here are 20 tips for living with alopecia areata:
- Join a support group
- Talk to a therapist
- Wear a wig or hairpiece
- Shave your head
- Focus on your positive qualities
- Don’t let AA define you
- Live your life to the fullest
- Remember that you are not alone
- There is hope for a cure for AA
- Be patient
- Be kind to yourself
- Don’t give up
- Educate others about AA
- Be an advocate for yourself
- Stay positive
- Have a sense of humor
- Find your inner strength
- Be grateful for what you have
- Live each day to the fullest
In conclusion
Alopecia areata is a challenging condition, but it is important to remember that you are not alone. There are many people who have AA, and there are a number of resources available to help you cope with the condition. With the right support, you can live a full and happy life with AA.
Tables
Table 1: Prevalence of Alopecia Areata
| Age Group | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| 0-19 years | 0.1% |
| 20-49 years | 1.1% |
| 50-69 years | 1.8% |
| 70+ years | 1.5% |
Table 2: Triggers of Alopecia Areata
| Trigger | Percentage of Cases |
|---|---|
| Stress | 20-30% |
| Illness | 10-15% |
| Certain medications | 5-10% |
| Trauma | 5-10% |
Table 3: Treatments for Alopecia Areata
| Treatment | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Topical medications | 50-70% | Skin irritation, itching, burning |
| Oral medications | 30-50% | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Light therapy | 60-80% | Sunburn, skin cancer |
| Surgery | 90-100% | Scarring, infection |
Table 4: Coping Mechanisms for Alopecia Areata
| Coping Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Joining a support group | Connecting with other people who have AA can provide support and understanding. |
| Talking to a therapist | A therapist can help you to understand your emotions and develop coping mechanisms. |
| Wearing a wig or hairpiece | A wig or hairpiece can help you to feel more confident about your appearance. |
| Shaving your head | Shaving your head can be a liberating experience and can help you to accept your AA. |