Unveiling the Color Wheel Spectrum
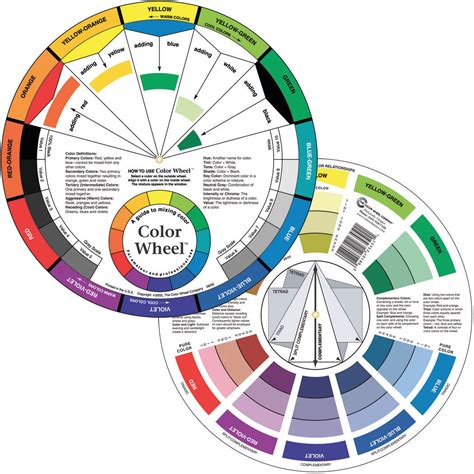
The hair color wheel is an essential tool for colorists and stylists seeking to create harmonious and visually appealing hair transformations. It provides a comprehensive visual representation of the relationships between different hair colors, enabling professionals to understand how these colors will interact when applied to hair.

The hair color wheel is typically divided into three primary colors: red, yellow, and blue. These colors cannot be created by mixing other colors and serve as the foundation for all other hair colors. Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors, such as orange (red and yellow), green (yellow and blue), and violet (red and blue). Tertiary colors are created by mixing a primary color with a secondary color, such as red-orange, blue-green, and yellow-green.
Understanding the Color Theory Principles
The hair color wheel operates on the principles of color theory, which govern how colors interact and create visual effects.
Color Harmonies: The color wheel can be used to identify colors that are harmonious, meaning they complement each other and create a visually pleasing effect. Analogous colors are colors that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel, such as red, orange, and yellow. Complementary colors are colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, such as red and green. Triadic colors are colors that are equally spaced apart on the color wheel, such as red, blue, and yellow.
Color Contrasts: Color contrasts are created by using colors that are far apart on the color wheel. This can create a striking visual impact but should be used with caution to avoid clashing or overpowering effects.
Neutral Colors: Neutral colors, such as black, white, and gray, can be used to tone down or balance other colors. They can also be used to create subtle highlights and lowlights.
Color Wheel Applications in Hair Coloring
The hair color wheel finds numerous applications in hair coloring, including:
Color Correction: By understanding how colors interact on the color wheel, colorists can neutralize unwanted tones or correct color mistakes. For example, if hair has turned brassy, a purple toner can be used to neutralize the yellow tones.
Custom Color Blending: The color wheel allows colorists to blend custom shades that match the client’s desired color or complement their skin tone. This enables them to achieve highly personalized hair transformations.
Hair Contouring: Colorists can use the hair color wheel to create depth and dimension in hair by strategically applying different colors. For example, a darker shade can be applied to the roots to create a shadow effect, while lighter shades can be used on the ends to brighten the look.
Creative Color Combinations: The hair color wheel inspires colorists to experiment and create unique and unconventional hair color combinations. By understanding how colors interact, they can push boundaries and achieve stunning results.
Tips and Tricks for Effective Hair Coloring
Consider Skin Tone: The client’s skin tone plays a crucial role in selecting flattering hair colors. Warm skin tones look best with warm colors, such as reds, oranges, and golds, while cool skin tones suit cool colors, such as blues, greens, and purples.
Test Before Application: Always perform a strand test before applying color to all hair. This will help you determine how the color will look and whether it will react adversely with the client’s hair.
Use Color-Safe Products: To maintain the vibrancy of colored hair, use color-safe shampoos, conditioners, and styling products. These products are formulated to protect hair from fading or becoming brassy.
Follow Proper Application Techniques: Ensure that color is applied evenly and thoroughly to achieve optimal results. Use color brushes and bowls designed for hair coloring and follow manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
Protect Hair Before and After Treatment: Apply a protein-rich hair mask before coloring to strengthen hair and prevent damage. After coloring, use heat protectants and avoid excessive heat styling to preserve hair health.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Hair Coloring
Color Clashing: Avoid using colors that are too far apart on the color wheel, as this can create a jarring or unflattering effect.
Overlapping Colors: Overlapping different colors can result in muddy or unpredictable results. Ensure that colors are applied cleanly and avoid mixing shades unnecessarily.
Incorrect Toning: Toners are used to neutralize unwanted tones or enhance color vibrancy. Choose the correct toner based on the color wheel and apply it precisely to avoid over-toning.
Excessive Bleaching: Avoid excessive bleaching, as this can damage hair and compromise its structural integrity. If necessary, use a gentler bleach or introduce lighter tones gradually.
Poor Aftercare: Failing to properly care for colored hair can accelerate fading or damage. Follow aftercare instructions carefully to maintain the health and vibrancy of your hair color.
Step-by-Step Hair Coloring Process
- Consultation: Discuss the client’s desired color, skin tone, and hair condition.
- Strand Test: Perform a strand test to determine the appropriate color and processing time.
- Hair Preparation: Wash hair with a clarifying shampoo to remove any product buildup or oils.
- Color Application: Apply color as per the manufacturer’s instructions, using color brushes and bowls.
- Processing: Allow the color to process for the recommended duration, monitoring the color change.
- Rinsing and Conditioning: Rinse hair thoroughly with cool water and apply a deep conditioning mask to nourish and seal the color.
- Styling: Style hair as desired and apply a color-safe product to enhance shine and protect from fading.
Color Wheel Tables for Hair Coloring Reference
Table 1: Color Wheel Primary and Secondary Colors
| Primary Color | Secondary Color |
|---|---|
| Red | Orange |
| Yellow | Green |
| Blue | Violet |
Table 2: Color Wheel Analogous Colors
| Base Color | Analogous Colors |
|---|---|
| Red | Orange, Red-Orange |
| Yellow | Yellow-Green, Green |
| Blue | Blue-Green, Violet |
Table 3: Color Wheel Complementary Colors
| Base Color | Complementary Color |
|---|---|
| Red | Green |
| Yellow | Violet |
| Blue | Orange |
Table 4: Color Wheel Triadic Colors
| Base Color | Triadic Colors |
|---|---|
| Red | Yellow, Blue |
| Yellow | Red-Orange, Violet |
| Blue | Orange-Yellow, Red-Violet |
Conclusion
The hair color wheel is an indispensable tool for hair colorists, empowering them to create harmonious and visually stunning hair transformations. By understanding the principles of color theory and applying the techniques outlined in this guide, hair professionals can achieve exceptional results and elevate their artistry.