Introduction
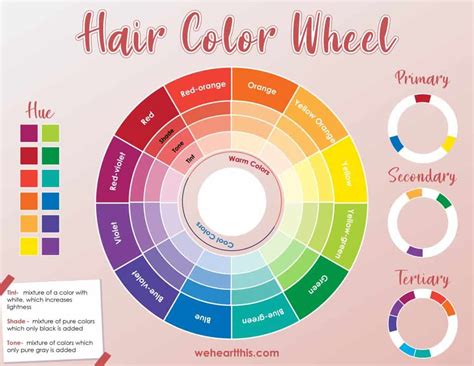
The hair color wheel is an indispensable tool for hair professionals and enthusiasts alike. It provides a systematic approach to understanding color theory and creating harmonious color combinations. By understanding the relationships between different hair colors, you can achieve a look that complements your natural features and enhances your overall style.

The Basic Colors
The hair color wheel consists of three primary colors (red, yellow, and blue), three secondary colors (orange, green, and purple), and six tertiary colors (red-orange, red-violet, blue-violet, blue-green, yellow-green, and yellow-orange). These colors are arranged in a ring, with the primary colors forming an equilateral triangle at the center.
Color Relationships
Complementary Colors: Complementary colors are those that are opposite each other on the color wheel, such as red and green or blue and orange. When placed side by side, these colors create a high-contrast effect that can be both visually striking and flattering.
Analogous Colors: Analogous colors are those that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel, such as red, red-orange, and orange. These colors blend together seamlessly, creating a harmonious and cohesive look.
Triadic Colors: Triadic colors are those that are evenly spaced around the color wheel, forming a triangle. For example, red, yellow, and blue are triadic colors. Using triadic colors in hair creates a dynamic and balanced effect.
Hair Color Theory in Practice
Choosing the Right Hair Color: When choosing a hair color, it is important to consider your skin tone, eye color, and personal style.
- Warm Skin Tones: Warm skin tones generally look best with hair colors that have red, orange, or gold undertones, such as copper, mahogany, or caramel.
- Cool Skin Tones: Cool skin tones generally look best with hair colors that have blue, green, or purple undertones, such as ash blonde, platinum, or silver.
Using Hair Toners: Hair toners are semi-permanent dyes that can be used to adjust the tone of your hair color. They can be used to warm up cool tones or cool down warm tones, and they can also be used to correct unwanted brassiness or orange tones.
Creating Highlights and Lowlights: Highlights and lowlights are techniques that involve adding lighter and darker shades of color to your hair. This can create depth and dimension, and it can also be used to frame the face or draw attention to certain features.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Choosing a hair color that is too far from your natural color: This can result in a look that is unnatural and unflattering.
- Over-toning your hair: Using too much hair toner can damage your hair and make it dry and brittle.
- Over-highlighting or lowlighting your hair: This can create a look that is too busy and distracting.
Conclusion
The hair color wheel is a powerful tool that can help you achieve a stunning and flattering hair color. By understanding color theory and following the tips in this article, you can create a look that complements your natural features and enhances your overall style.